Not long ago I posted a series of myths and realities about Agile on my LinkedIn account. While many in the business world talk about Agile ways of working, how accurate is the information we think we know? Are you confusing an Agile myth with reality? In June, I shared an article on the Agile Mindset and what a person needs to truly be agile. I would like to follow up by sharing my top 6 Agile myths:

MYTH #1: AGILE IS A SET OF PROJECT MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORKS
REALITY: Agile is primarily a culture, a way of thinking and acting.
- The biggest and most common mistake and the reason that many fail at implementing Agile in organizations comes from focusing on the DOING Agile without working on the BEING Agile.
- Implementing Scrum, Design Thinking, Hackathons, Lean, Kanban and other Agile frameworks will not be sufficient to be Agile.
MYTH #2: LEADERS ARE NOT NEEDED IN AGILE
REALITY: True…and false.
- Agile needs leaders, but not where they might usually spend their time and energy.
- Their role is to drive and foster the appropriate ecosystem and culture. They must genuinely inspire themselves first and then their people with a compelling Purpose, Vision, and Strategy that can guide decisions and actions. This is not a minor role. An Agile organization could not exist without these leaders.
- In Agile, coaching leaders to empower their people by decentralizing decisions, control, and accountability to the point closest to action.
- To put it in other terms, leaders move from the pilot seat to the co-pilot one.
- Top management is often unconsciously the main barrier or intentionally the key enabler of BEING Agile more than being directly involved in Agile projects.
Myth #3: AGILE IS BETTER AND FASTER. Its role is to increase the speed of decisions and actions.
REALITY: Speed of decision and action is part of a predefined daily and weekly planning but is not a goal. Value delivery to customers comes before timing.
Myth #4: AGILE IS ABOUT PRODUCING MORE, QUICKER, AND CHEAPER
REALITY: Big mistake. Agile optimizes value delivery and customer satisfaction first, not just productivity and efficiency.
Myth #5: AGILE IS PERMANENT INSTABILITY MANAGEMENT
REALITY: Agile’s pre-defined cadence and framework are highly predictable. You know in real-time how the team is tracking against objectives with daily baby steps, one at a time, with clear objectives. This approach makes manageable permanent changes and instability with iterative adaptations, learning and improving from mistakes/successes with clear metrics from customer feedback.
Myth #6: WE DON’T NEED AGILE COACHES. Agile Coach = Scrum Master
REALITY: Agile is about people before processes and the Agile Coach is here to help the team adopt effective mindsets and behaviors individually and as a team: Agile is a way of thinking, acting, and interacting.
- The functions of a Scrum Master are to carry out all those projects that use a Scrum methodology from the elaboration of the product backlog, sprint backlog, the sprint itself, and the burndown of the tasks carried out and everything that remains pending.
Conclusion
Agile does not have to be a buzzword. It is what you need it to be. don’t copy/paste what others do. Find what works in your organization. BE the agility you want to see in your organization: Agile is not a destination it is a mindset and a way of working together.

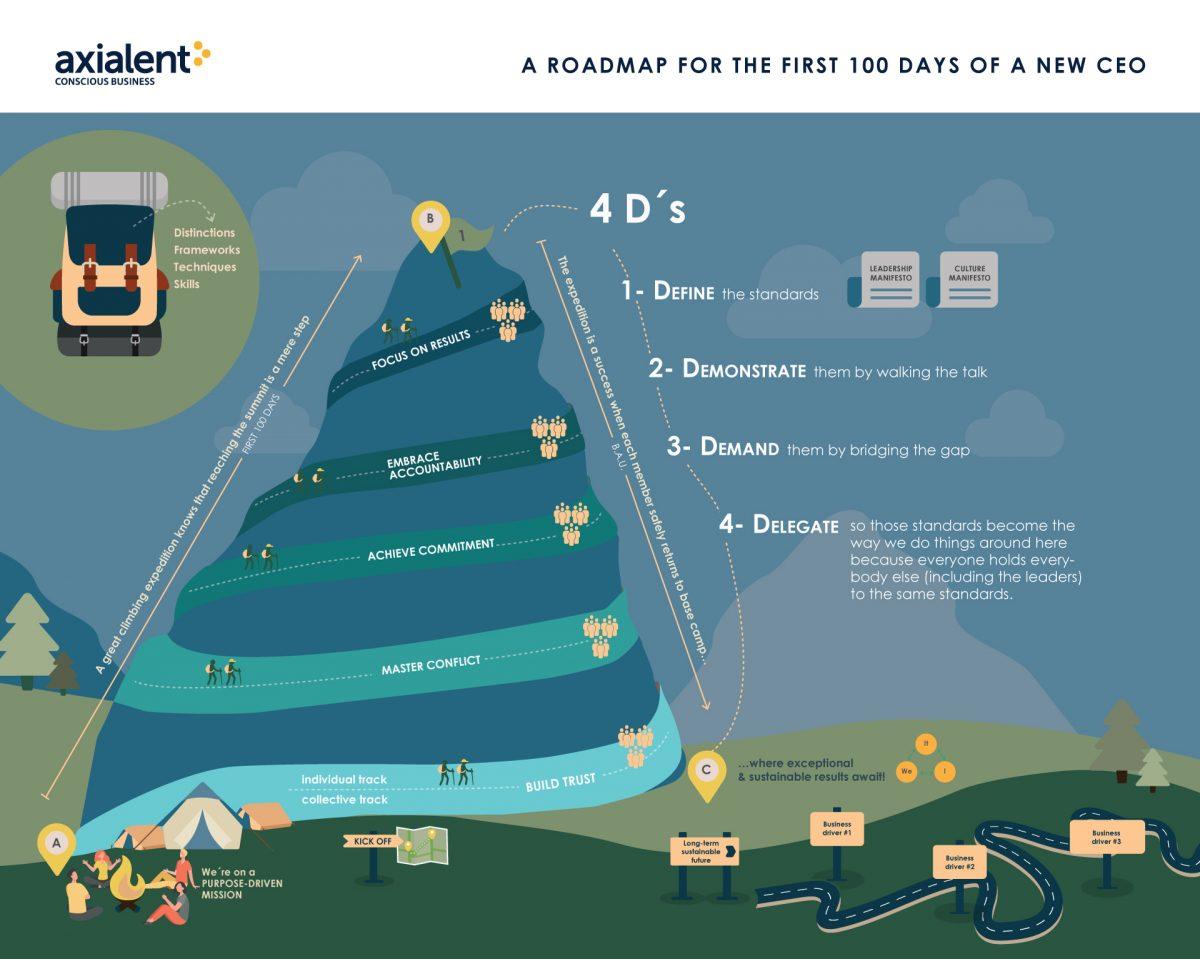
 Beginnings, or new beginnings, are exciting. They create momentum, but it’s a hard job to keep the flame alive. If the leadership team does an excellent job with the four D’s mentioned in article two, there’s a higher chance that the flame will last longer. However, they will need a sustainable fuel source for that flame because eventually, it will die out. No matter how well-intended the leaders are, their behaviors are not enough to consolidate an evolving or transforming culture. Culture needs to be hinged on systems to endure.
Beginnings, or new beginnings, are exciting. They create momentum, but it’s a hard job to keep the flame alive. If the leadership team does an excellent job with the four D’s mentioned in article two, there’s a higher chance that the flame will last longer. However, they will need a sustainable fuel source for that flame because eventually, it will die out. No matter how well-intended the leaders are, their behaviors are not enough to consolidate an evolving or transforming culture. Culture needs to be hinged on systems to endure.
 One of the first outcomes of the leadership team journey described in the
One of the first outcomes of the leadership team journey described in the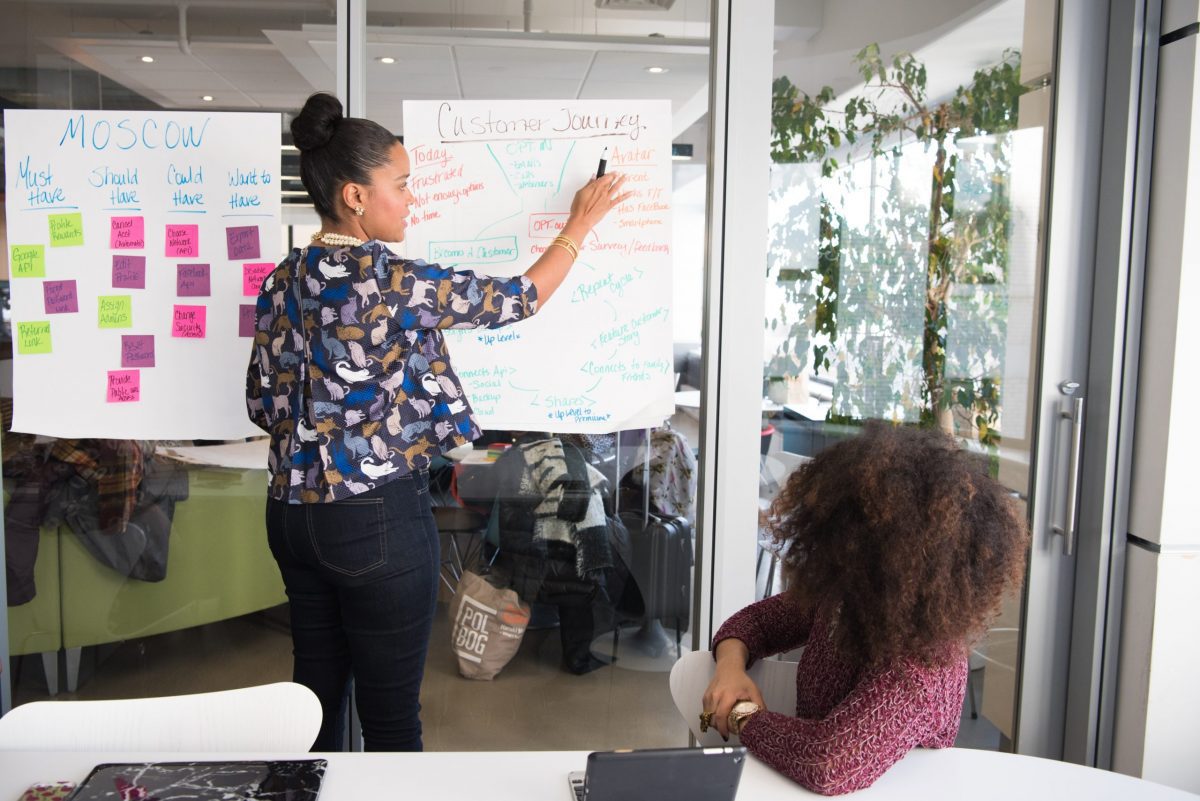 
 It is about PROACTIVELY CREATING change in uncertain and disruptive environments. Different from resilience, it is about REACTIVELY RESPONDING to change in a constructive way.
It is about PROACTIVELY CREATING change in uncertain and disruptive environments. Different from resilience, it is about REACTIVELY RESPONDING to change in a constructive way.
 This is precisely how innovation in a corporation works. It is a hard job, with multiple tasks and things to do. You might be working on designing a new solution, defining the precise value proposition, and trying to get the buy-in from different stakeholders. Suddenly, an apparently simple problem is holding things up, and you might feel like it is the end of the world. You feel shame. You question your value, your capabilities, your management skills, or even your work.
This is precisely how innovation in a corporation works. It is a hard job, with multiple tasks and things to do. You might be working on designing a new solution, defining the precise value proposition, and trying to get the buy-in from different stakeholders. Suddenly, an apparently simple problem is holding things up, and you might feel like it is the end of the world. You feel shame. You question your value, your capabilities, your management skills, or even your work.


 Allow me to emphasize this fourth lesson for a moment. Agile is often presented as the remedy that will heal all corporate ailments. This is overly simplistic, and some may even consider it an insult to their intelligence. However, the natural tendency of this person is to sway to the other end of the pendulum and negate any benefit of the new way of working. This, too, is foolish.
Allow me to emphasize this fourth lesson for a moment. Agile is often presented as the remedy that will heal all corporate ailments. This is overly simplistic, and some may even consider it an insult to their intelligence. However, the natural tendency of this person is to sway to the other end of the pendulum and negate any benefit of the new way of working. This, too, is foolish.

 The second aspect that made this program different was that it was not designed as the typical immersive, residential, intensive x-day workshop. Instead, we scheduled shorter interventions several weeks apart. This design was deployed before the pandemic, so the sessions were held face-to-face. Nevertheless, this concept has survived to this day as a valid structure for most of our hybrid or purely online leadership development journeys.
The second aspect that made this program different was that it was not designed as the typical immersive, residential, intensive x-day workshop. Instead, we scheduled shorter interventions several weeks apart. This design was deployed before the pandemic, so the sessions were held face-to-face. Nevertheless, this concept has survived to this day as a valid structure for most of our hybrid or purely online leadership development journeys.

